Energy Saving Opportunities in the HVAC System
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are essential for maintaining indoor comfort. However, they are also among the largest energy consumers in homes and commercial buildings. If you've ever wondered, “Does AC affect the electric bill?” the answer is a resounding yes. Fortunately, there are several strategies to enhance your HVAC system's efficiency, leading to significant energy savings without compromising comfort.
1. Upgrade to a High-Efficiency Centralized AC System
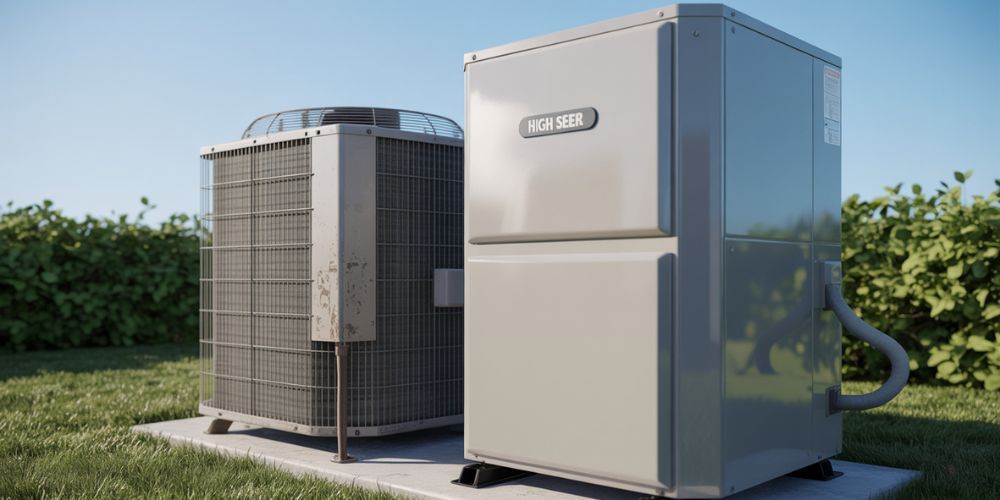

If your air conditioner is over 10–15 years old, it may be operating inefficiently, leading to higher energy bills. Upgrading to a centralized AC system with a high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating can reduce cooling energy consumption by 15–20% compared to standard models.
Understanding the main components of an HVAC system can help you make informed decisions about upgrades and maintenance.
2. Utilize Smart Thermostats for Automated Efficiency
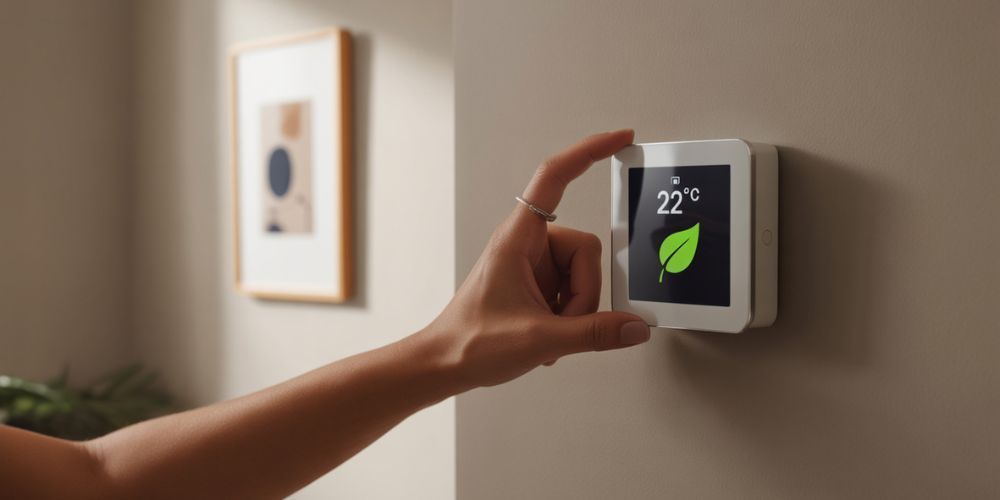

Smart thermostats are invaluable tools for optimizing HVAC energy usage. They learn your behavior over time, adjusting temperatures automatically to save energy when you're asleep or away. Additionally, they provide usage reports and mobile control, allowing you to fine-tune settings based on real-time data.
3. Seal and Insulate Ductwork
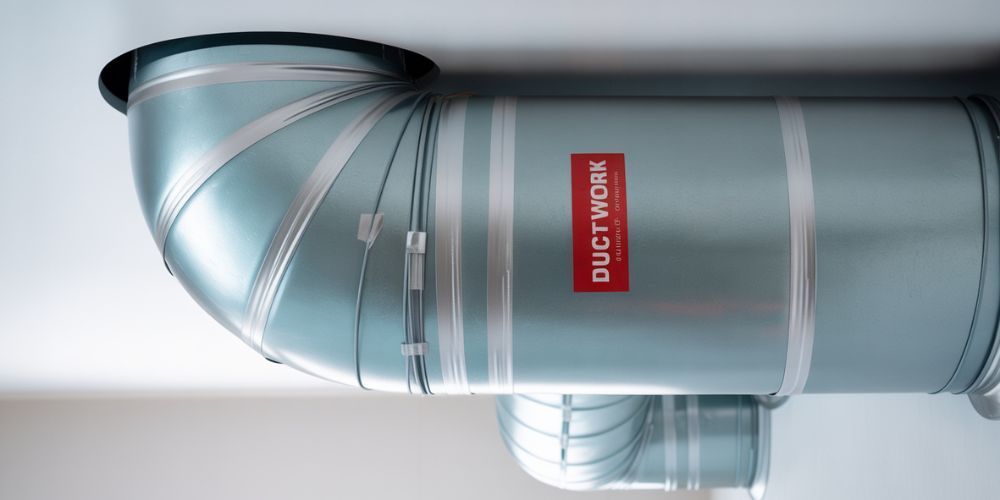

Leaky or poorly insulated ducts can lead to significant energy losses. Sealing and insulating your ductwork ensures that conditioned air reaches its intended destination efficiently, reducing energy waste and improving comfort.
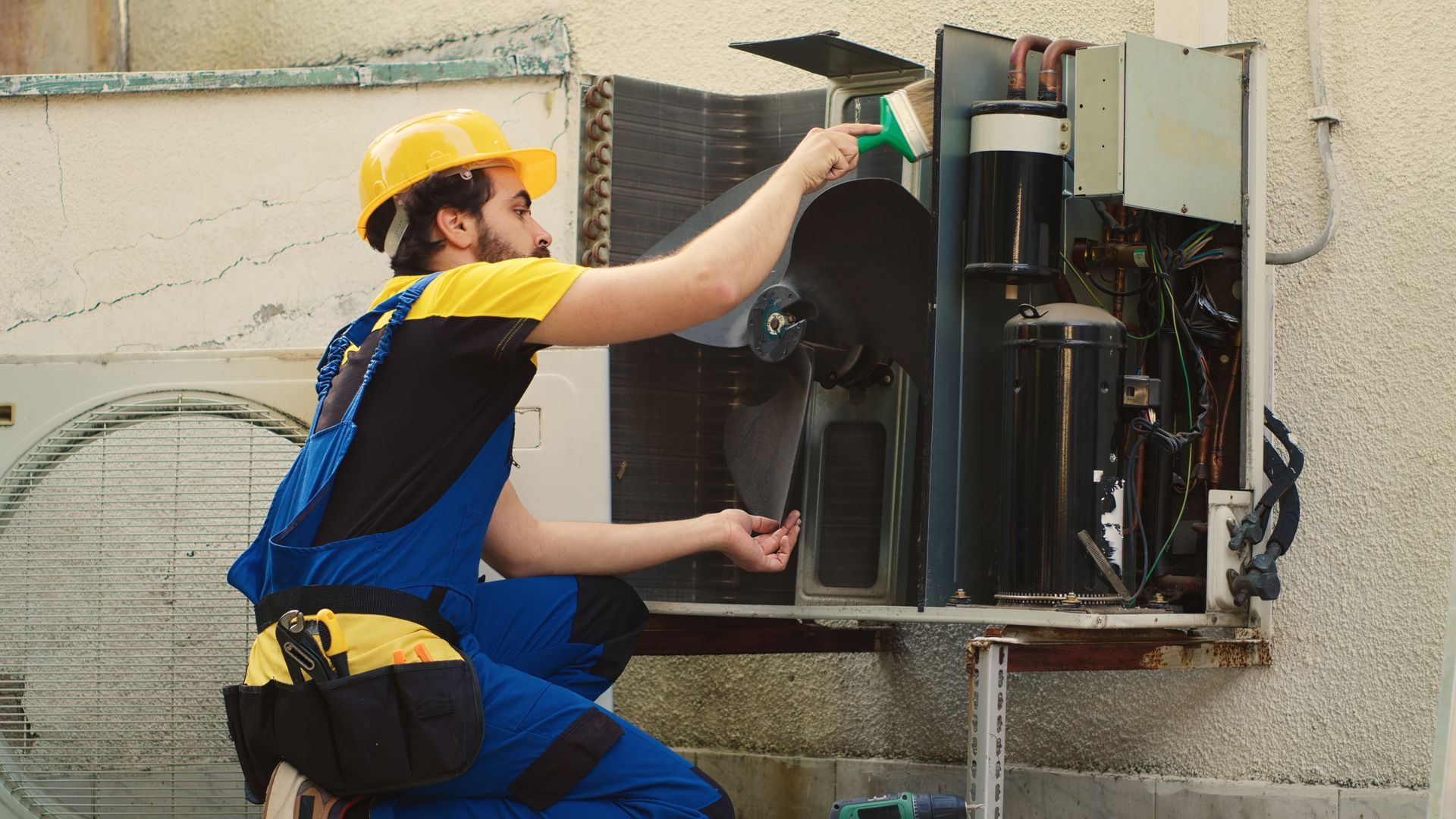
4. Regular HVAC Maintenance: Small Fixes, Big Impact
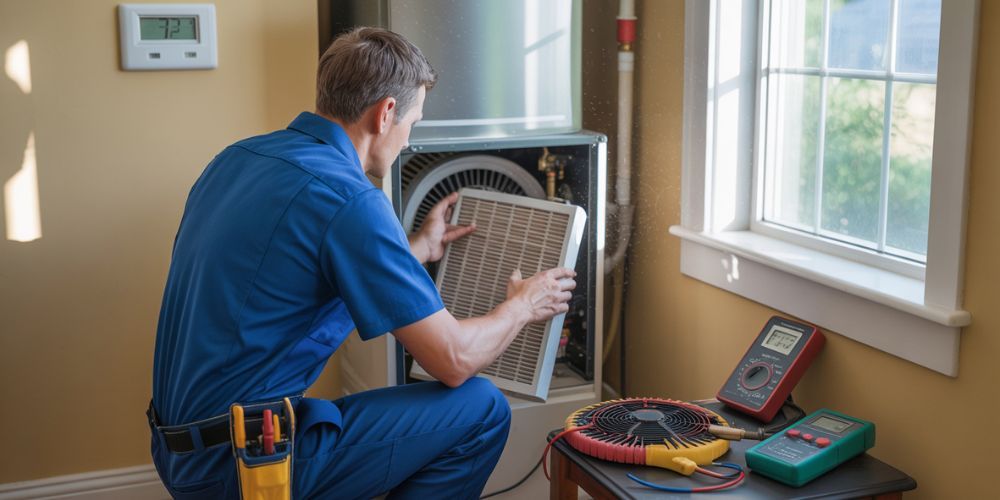

Preventive maintenance is crucial for keeping your HVAC system running efficiently. Regular tasks include:
- Replacing filters every 1–3 months
- Cleaning the evaporator and condenser coils
- Checking and topping off refrigerant levels
- Inspecting blower components for proper airflow
- Ensuring thermostat accuracy
Refer to our HVAC maintenance checklist for a comprehensive guide to maintaining your system year-round.
5. Implement Zoning Systems
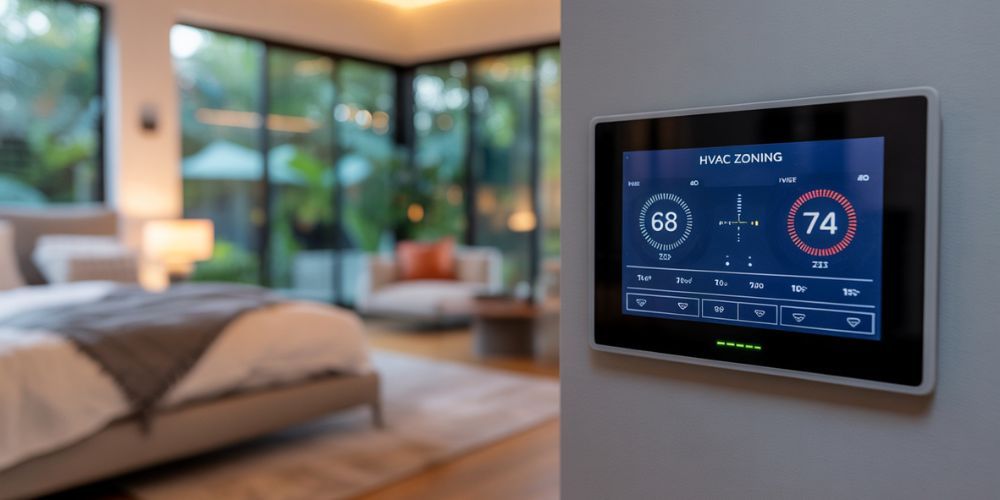

Zoning allows you to control temperatures in specific areas of your home or building, directing HVAC resources where they're needed most. This approach prevents energy waste by avoiding unnecessary heating or cooling of unoccupied spaces.
6. Enhance Ventilation and Airflow
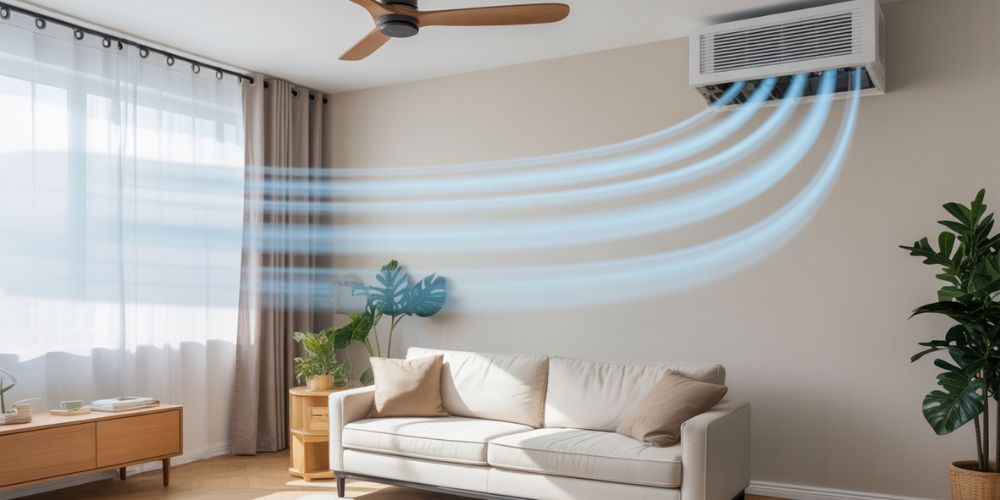

Poor airflow forces your HVAC system to work harder, increasing energy consumption. Improving airflow can be achieved by:
- Unblocking air vents
- Upgrading to variable-speed blowers
- Installing ceiling fans to circulate air
- Using energy recovery ventilators (ERVs)
Learn more about the importance of a proper ventilation system and how it contributes to energy efficiency.
7. Optimize Thermostat Settings
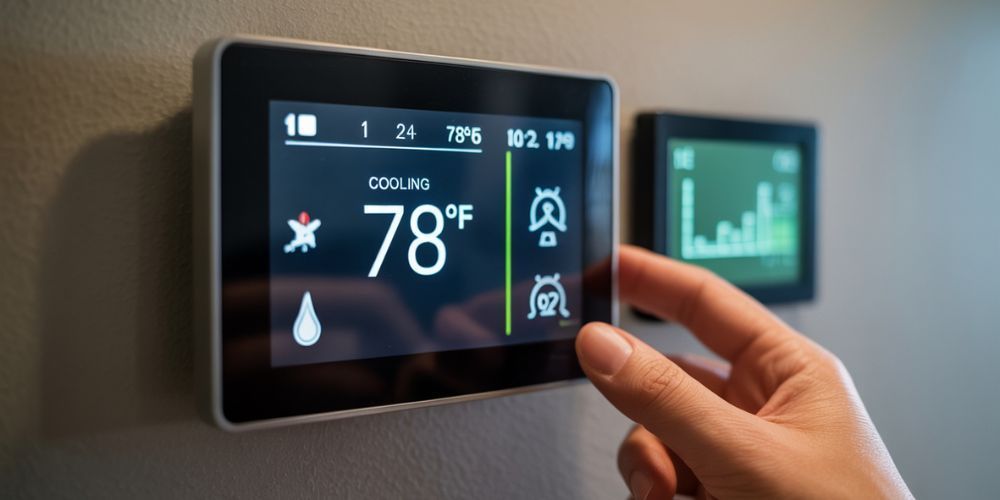

Small adjustments to your thermostat can lead to significant energy savings. The U.S. Department of Energy recommends:
- Setting the thermostat to 78°F (25.5°C) in summer when you're home
- Raising it to 85°F (29.5°C) when you're away
- Lowering it to 68°F (20°C) in winter
- Each degree of adjustment can save up to 3% on energy costs.
8. Choose Energy-Efficient HVAC Equipment
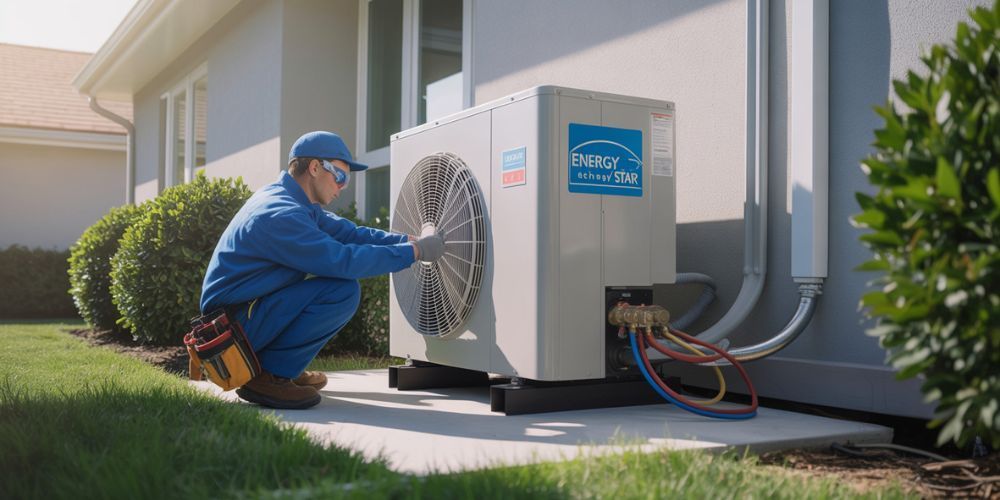

When purchasing HVAC equipment, look for the ENERGY STAR® label, indicating products that meet strict energy efficiency guidelines. Whether it's a new centralized AC system, heat pump, or furnace, selecting energy-efficient models will result in long-term savings.
Common Questions About HVAC Energy Use
1. Does AC affect the electric bill?
Yes, air conditioning significantly contributes to electricity usage, especially in hot climates or poorly insulated homes.
2. Is air conditioning part of the electric bill?
Absolutely. Unless powered by an alternative energy source, your AC's consumption is reflected in your monthly electric bill.
3.Does AC use gas or electricity?
Most air conditioning systems use electricity to power components like compressors and fans. Gas is typically used in HVAC systems for heating purposes.
4. Is A/C gas or electric?
In most cases, A/C systems are electric. Some HVAC systems may have a gas-powered furnace component, but the air conditioning side is powered by electricity.
5. Does central AC use a lot of electricity?
Central AC systems can consume significant electricity, especially if they're old or poorly maintained. However, modern energy-efficient models, combined with smart thermostats and proper insulation, can substantially reduce electricity use.
Reduce Costs by Optimizing Your HVAC System
HVAC systems don’t have to be energy hogs. By understanding how your system works and applying the strategies outlined in this guide, you can improve efficiency, lower your utility bills, and extend the lifespan of your equipment. Whether you’re considering an upgrade to a centralized AC, curious about how much electricity your AC uses, or figuring out whether your system runs on gas or electricity, the key is staying informed and proactive.
At KJ’s Heating and Air, we’re dedicated to helping you make smarter, energy-efficient choices without sacrificing comfort. With the right guidance and professional support, optimizing your HVAC system becomes an achievable goal — one that saves you money and keeps your home comfortable year-round.