How Often Should You Schedule HVAC Repairs and Maintenance?
HVAC systems require regular attention to maintain performance and avoid unexpected failures. This article explains recommended maintenance intervals, what each service type includes, and how scheduling decisions affect system longevity and repair costs.
How Often Should Residential HVAC Systems Be Serviced?
Most HVAC manufacturers and industry standards recommend professional maintenance twice per year—once before the cooling season and once before the heating season. This schedule aligns with the operational demands placed on different system components throughout the year.
Standard maintenance intervals include:
- Air conditioning inspection and tune-up in spring (March through May)
- Heating system inspection and tune-up in fall (September through November)
- Filter changes every 1-3 months, depending on system type and household conditions
- Thermostat calibration checks during seasonal service visits
- Refrigerant level verification during cooling system maintenance
- Combustion analysis for gas furnaces during heating season preparation
Systems operating in high-use environments or regions with extreme temperatures may require more frequent attention. Buildings in coastal areas often experience accelerated component wear due to salt air exposure, while properties in desert climates face increased strain from dust and sustained high-temperature operation.
What Does Preventive Maintenance Actually Include?
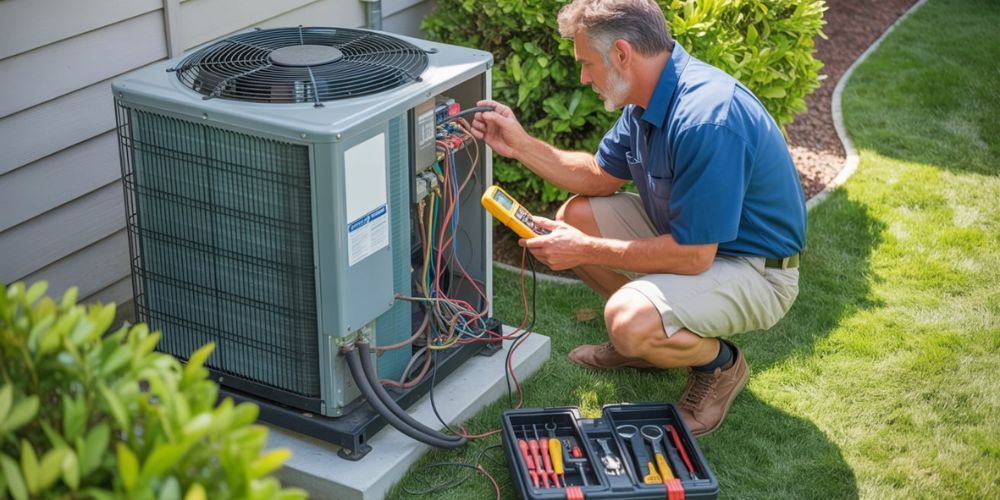
Preventive maintenance involves systematic inspection, cleaning, and adjustment of HVAC components before problems develop. Technicians follow manufacturer specifications and industry protocols to verify that each system element functions within acceptable parameters.
Typical maintenance tasks include:
- Cleaning or replacing air filters and checking filter housing integrity
- Inspecting electrical connections and measuring voltage and amperage
- Lubricating motors and bearings, where applicable
- Checking refrigerant pressures and temperatures
- Cleaning condensate drains and verifying proper drainage
- Inspecting ductwork connections and sealing visible leaks
- Testing safety controls and limit switches
- Measuring airflow and adjusting blower components if needed
The specific procedures vary based on equipment type, age, and manufacturer requirements. Split systems require different attention than packaged units, and variable-speed equipment needs different diagnostic approaches than single-stage systems. Documentation from these visits creates a service history that helps identify developing patterns before they cause system failure.
When Should You Schedule Repairs Instead of Waiting for Maintenance?
HVAC Repairs become necessary when system performance degrades or components fail between scheduled maintenance visits. Certain symptoms indicate problems that will worsen without intervention, while others suggest safety concerns requiring immediate attention.
Signs requiring prompt repair service:
- Unusual noises such as grinding, squealing, or banging from equipment
- Reduced airflow from supply registers throughout the building
- Inconsistent temperatures between rooms or zones
- Visible ice formation on refrigerant lines or coils
- Water pooling near indoor equipment or frequent drain pan overflow
- Burning odors or electrical smells from vents or equipment
- System cycling on and off more frequently than normal
- Unexplained increases in energy consumption without usage changes
Addressing these issues when they first appear typically costs less than waiting for a complete system failure. Components that fail often cause secondary damage to related parts, expanding repair scope and expense. A failing compressor, for example, may send debris through refrigerant lines that damages other system elements.
How Does Equipment Age Affect Maintenance Frequency?
HVAC systems require more frequent attention as components age and wear accumulates. Equipment in its first five years typically performs reliably with standard twice-yearly maintenance, while systems beyond ten years often benefit from additional monitoring.
Age-related maintenance considerations:
- Systems over 10 years old may need tri-annual inspections
- Older equipment experiences higher failure rates for capacitors and contactors
- Refrigerant leaks become more common as joint seals age
- Heat exchanger inspection becomes critical in furnaces over 15 years old
- Compressor performance should be monitored more closely after 12-15 years
- Blower motors and fan assemblies show increased wear after extended service
Manufacturers design residential HVAC equipment for approximately 15-20 years of service under normal conditions. Systems approaching or exceeding this age range require careful evaluation during each maintenance visit to determine whether continued repair remains cost-effective compared to replacement.
What Happens When Maintenance Is Skipped or Delayed?
Deferred maintenance allows minor issues to progress into significant problems while reducing overall system efficiency. Components that would receive cleaning and adjustment during scheduled service instead of accumulating dirt, experience increased friction, and operate outside optimal parameters.
Consequences of inconsistent maintenance:
- Reduced heat transfer efficiency as coils accumulate dirt and debris
- Increased energy consumption as the system works harder to maintain temperatures
- Shortened component lifespan due to increased operating stress
- Higher likelihood of mid-season failure during peak demand periods
- Voided equipment warranties that require documented professional service
- Reduced indoor air quality as filtration effectiveness decreases
- Increased risk of refrigerant leaks going undetected until a major loss occurs
The financial impact of skipped maintenance often exceeds the cost of scheduled service. A system operating with dirty coils may consume 20-30% more energy while providing less effective temperature control. Emergency repairs during extreme weather typically cost more than the same repairs performed during moderate conditions.
How Do Commercial Systems Differ in Maintenance Requirements?
Commercial HVAC equipment operates under different demands than residential systems and requires adjusted maintenance schedules. Larger capacities, extended operating hours, and higher occupancy loads accelerate wear and increase the importance of consistent service intervals.
Commercial maintenance considerations:
- Monthly filter changes are common in high-occupancy buildings
- Quarterly maintenance visits for rooftop units and large packaged systems
- More frequent belt inspections and replacements on commercial air handlers
- Regular calibration of economizers and advanced control systems
- Priority scheduling to minimize business disruption
- Documentation requirements for building management and compliance
- Coordination with facility managers and occupancy schedules
Commercial buildings often maintain service agreements that provide scheduled maintenance plus priority response for repair needs. The cost of system downtime in commercial applications - through lost productivity, uncomfortable conditions for customers, or spoiled inventory - typically justifies more aggressive maintenance approaches than residential properties require.
What Role Does Climate Play in Maintenance Scheduling?
Regional climate conditions directly affect HVAC maintenance requirements and appropriate service timing. Areas with distinct seasonal changes follow different protocols than locations with year-round cooling demands or minimal heating needs.
Climate-based scheduling factors:
- Year-round cooling climates require more frequent condenser coil cleaning
- Coastal environments need corrosion inspection and protective treatments
- High-humidity regions require more attention to condensate drainage systems
- Desert climates demand increased air filtration and outdoor unit protection
- Areas with mild winters may reduce heating system maintenance frequency
- Regions with temperature extremes benefit from pre-season equipment testing
Properties in Southern California face specific considerations based on coastal proximity and temperature patterns. Inland areas experience greater temperature swings requiring both heating and cooling system attention, while coastal properties may operate cooling equipment nearly year-round with minimal heating demand.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does typical HVAC maintenance cost?
Residential maintenance visits typically range from $80 to $150 per visit for standard service. Commercial maintenance costs vary significantly based on equipment size and complexity.
Can I perform HVAC maintenance myself?
Homeowners can change filters and keep outdoor units clear of debris, but professional maintenance requires specialized tools, refrigerant certification, and technical knowledge to properly inspect and adjust system components.
Does maintenance really prevent repairs?
Regular maintenance identifies developing problems before they cause failure and keeps components operating efficiently, which reduces stress and extends service life. However, it cannot prevent all repairs as components eventually wear out.
What voids an HVAC warranty?
Most manufacturers require documented professional maintenance at specified intervals. Lack of maintenance records, use of uncertified technicians, or improper refrigerant handling typically voids warranty coverage.
How long does a maintenance visit take?
Standard residential maintenance visits typically require 60-90 minutes for a thorough inspection and service of a complete system. Commercial equipment requires more time based on size and complexity.
A Final Thought
HVAC maintenance requirements reflect the balance between operational demands, equipment condition, and environmental factors specific to each property. Regular service intervals prevent most unexpected failures while providing opportunities to address developing issues before they escalate. Adjusting maintenance frequency based on system performance and age helps optimize both equipment longevity and operational costs.